characterization of on-road traffic emissions in the center of Valencia

OPUS RSE developed a project in the city center of Valencia, Spain, to meassure the real-driving emissions of motor vehicles in urban streets of the city.
This project was done for the department of Air Quality of Valencia City Council.
measuring real emissions in the city center under different traffic conditions
In October 2018, OPUS RSE moved to Valencia to measure the emissions from motor vehicles. The aim of the project was to measure in different roads with different traffic conditions and to obtain a general view of the emissions from the vehicles fleet of the city. The project also carried out a study of the total contribution of High Emitters to air quality.
At the end of the project OPUS RSE delivered a comprenhensive set of data and conclussions of the emissions of different types of vehicles.
Thanks to the mobility capacity of the Opus RSD, the devices was deployed in different streets of the city center without any road modification neither interferience to traffic.
An informative panel, which shows the emissions of each vehicle in real-time, was deployed on the streets, so that the drivers could see how much their vehicle emitted in as they drive by. The notification has a comprenhensive semaphore -like alert; green forLow Emissions, yellow for Medium Emissions and red for High Emissions.
Location
The RSD meassured the emissions of the vehciles of Valencia in different sites of the city center.
FIELD CAMPAIGN
Results
Most of the measured vehicles were Passenger Cars (between 80 and 90%) and among all types of vehicles 66,4% were diesel and 32,3% were gasoline.
4 pollutants were measured by the RSD: NOx, CO, HC and particulate matter, PM.
The conclussions of the project were that diesel buses and trucks had the higest emissions in NOx and PM whereas the gasoline motocicles had the higest average of CO and HC emissions (more than two times the average of the rest of the vehicles). However, as Passenger Cars are the most common vehicle in the city, they are responsible for most of the total emissions.
It was found that most of diesel Passenger Cars exceeded the Euro Limits in NOx, even Euro 6 (newest vehicles). Also, the HC average from all vehicles (gasoline and diesel) exceeded the limits. In general, the CO emissions from gasoline vehicles are higher than diesel vehicles, and finally, diesel vehicles PM emissions are significantly higher than gasoline.
So as a 86% of the vehicles measured were passenger cars, the next figure shows a comparison between diesel and gasoline PC vehicles according to their Euro Standard.

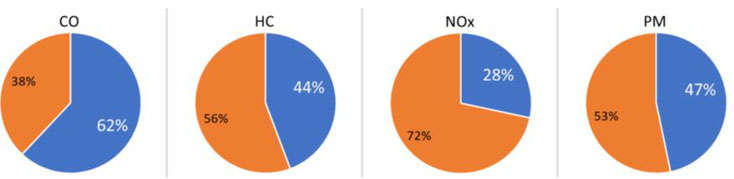
In this project, OPUS RSE also made a study based on the identification of High Emitters. Those are vehicles that emit much more than the rest of the fleet. It was determined that they contribute between 28% and 62% to total emissions of each pollutant, as it can be observed on the figure below. The blue part correspond to the High Emitters' contribution to total emissions and the orange one to the rest of the fleet.